Discover how to run apps as an administrator on Mac to access root privileges and perform critical tasks. Running an app as an administrator will allow the user to access the app from root privileges. It does not need until you need to do some really important task in the app.
If you don’t know about the root usage of an app then don’t run it as an administrator as it may cause serious damage to the application. Follow the guide to learn how to run apps as an administrator on Mac.
Let’s get into it
How to Run Apps as an Administrator on Mac
Some apps allow you to root access the files of the application while some do not allow this. Many graphical applications don’t allow root access to the app. You can use this procedure on any other app rather than Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, or any similar apps.
1. From an Admin Account
If you are the admin of the Mac then you can easily run apps as an administrator on Mac. Make sure you limit yourself to some specific tasks that you know how to handle. Also, be aware of changing any setting in the app during root privilege.
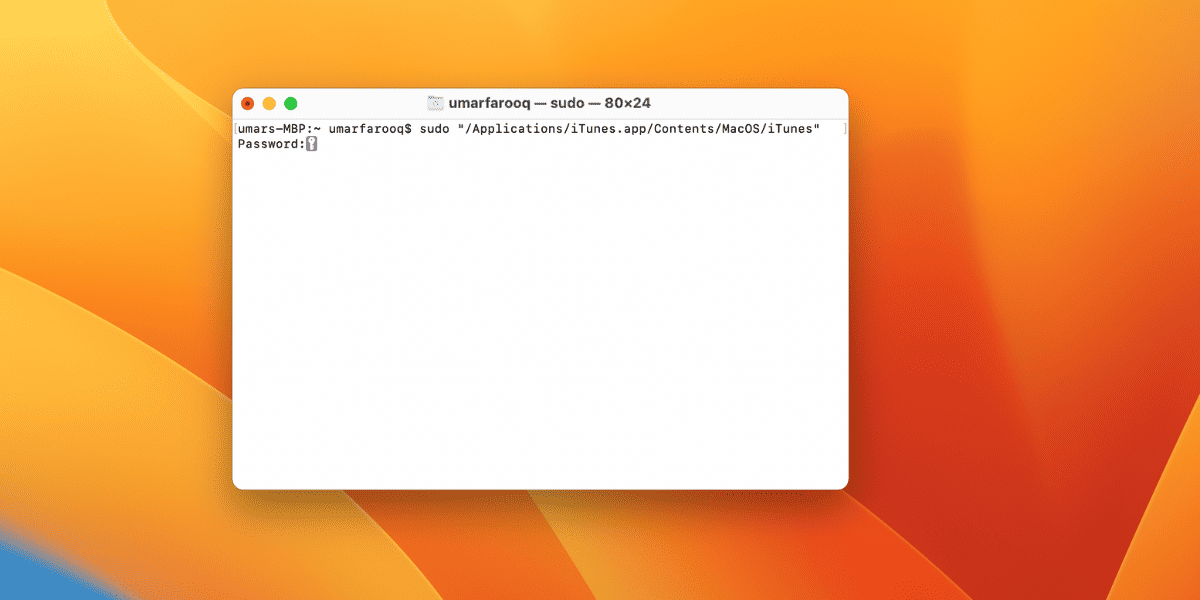
Here are the steps to do this:
- Log in to the Mac using the admin account.
- Go to Applications and Select Utilities.
- Launch the Terminal app.
- Enter sudo sudo “\file path from hard drive to application. app/Contents/MacOS/application name”. For example, to open iTunes, type sudo “/Applications/iTunes.app/Contents/MacOS/iTunes, and press Return.
- Now, enter the password of the current admin account and press enter.
- The application will be opened with the root privileges otherwise terminal will says “Command not found“.
If the application does not open with the root privileges and the terminal says command not Found then follow the next method.
Related:
How to Extract EXE Files on Mac
2. Drop Exe into Terminal
If the first method does not work well, you can try the second method to run apps as an administrator on Mac. Follow the below steps to perform it.
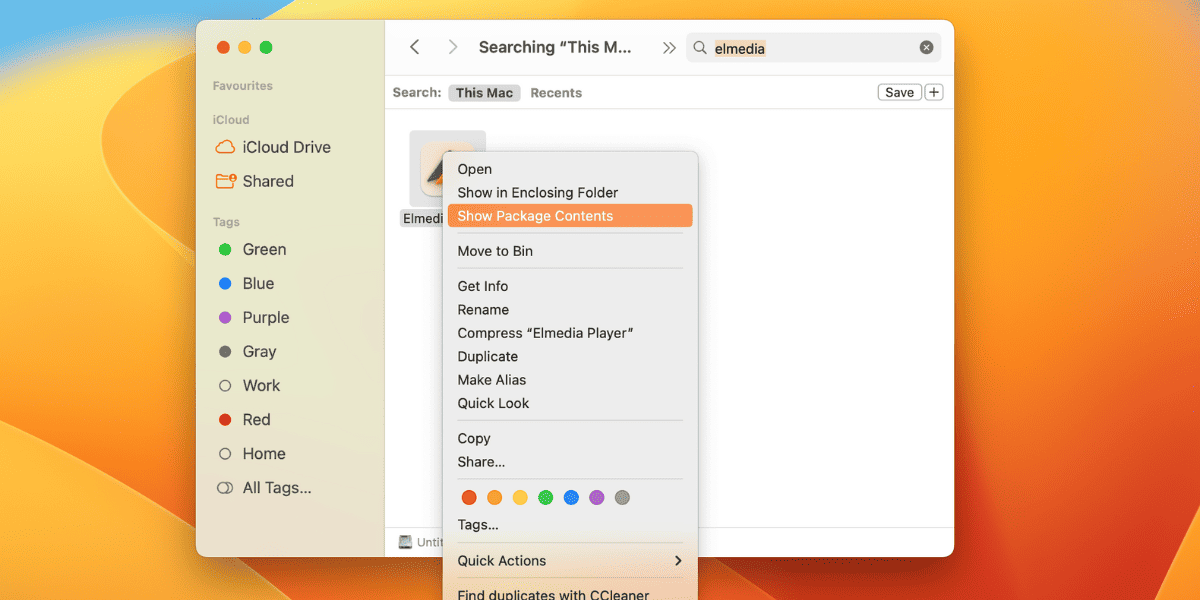
- In Finder, locate the application that you want to run as an administrator on Mac.
- Right-click on the app and click Show package contents from the drop-down options.
- This will open a folder with the Contents folder.
- In the contents, open the macOS folder and there you will find the executable file with the application name.
- Now, open the terminal using the above method and type Sudo followed by the space.
- Drag the exe file of the application from the macOS folder.
- It will add the path of the application. Hit the Return button.
- The terminal will confirm the admin password. Write the password and again hit return.
This will run the application as an administrator with the root privileges. Now, you can do whatever you want but make sure you know what you are doing. If you do anything wrong it will make the application inaccessible, application crashes, or vulnerabilities.
3. From Non-Admin Account
People mostly prefer to work in an ordinary account rather than an administrator account. This reduces the damage of the mistakes that happen during the troubleshooting of apps. The Non-admin account method allows users to get root privileges in ordinary user accounts.
Here’s how to get into it.
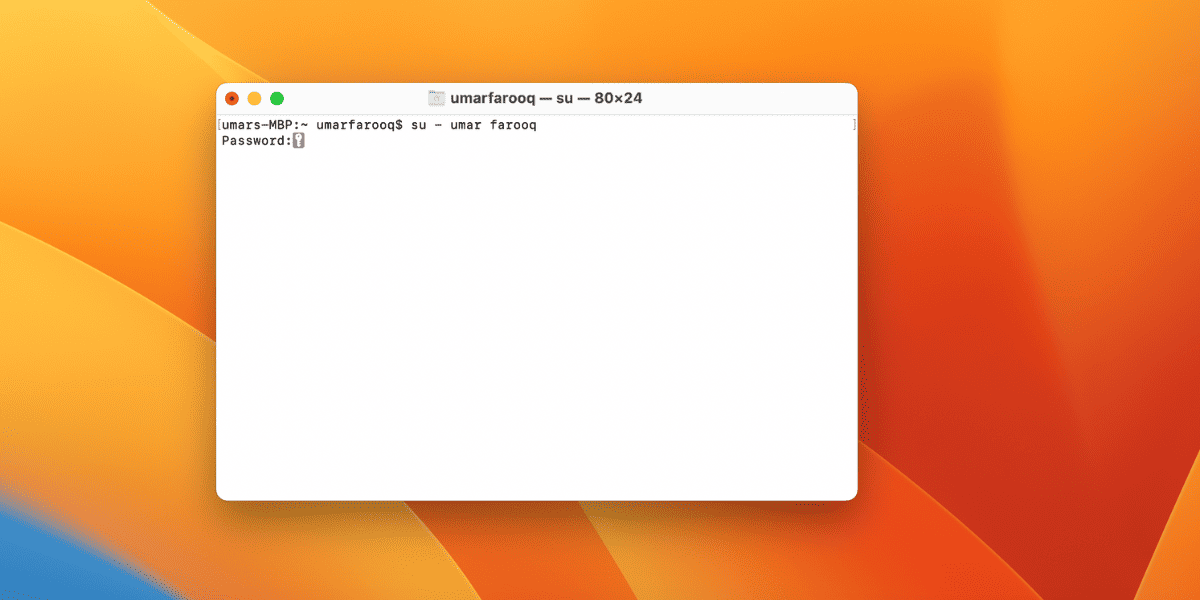
- Launch the terminal app with the user account.
- Enter the command: su – followed by a space and username of the administrator account.
- The terminal will ask for the password of the admin. Write the password.
- Now, open the application using sudo “\file path from hard drive to application. app/Contents/MacOS/application name”. For example, to open iTunes, type sudo “/Applications/iTunes.app/Contents/MacOS/iTunes, and press Return.
- This will open the app as an administrator.
- Now, write Exit in the terminal and hit Return to go back to your account.
If this method does not work then try the Drop Exe into the terminal method using the non-admin account.
Related:
How to Change Directory in Terminal on Mac
4. Troubleshooting
If you are unable to access the root privileges of any application using the above methods then try to disable the SIP. SIP is called System Integrity Protection. SIP was introduced in macOS 10.11, it limits access to important files for the user.
Sip also does not allow the admin to access the important files of the application. You can disable the SIP if you were unable to run apps as an administrator on Mac.
Warning: Make sure you are confident and understand that any mistake can wipe your computer or make it nonfunctional for you.
- Enter the recovery mode by restarting your Mac and holding the Command + R on the start-up noise.
- Select utilities > Terminal in the recovery mode.
- Write csrutil disable; reboot in Terminal.
- Restart the Mac as normal and your SIP will be disabled.
- Now, run apps as an administrator on Mac using any of the above methods.
After completing the task, you should enable the SIP with the same steps. You just need to change the disabled word with the enable to enable the System Integrity Protection.
Conclusion
These are four methods to run apps as an administrator on Mac. All the methods are easy to use but make sure you do the whole steps as written. Also, you must know what you want to do after getting the root privilege of an application.
